Proxification Rules
This feature allows you to define how certain connections should be processed by Proxifier. Each connection can be processed directly, through a proxy/chain or blocked.
The rules can be based on application names, the target host IP or address and port numbers. Applications and targets can be specified as wildcards. Ports can be specified as ranges.
To access this feature, click Proxification Rules in the Profile menu or the corresponding item on the toolbar:
The following dialog window will appear:
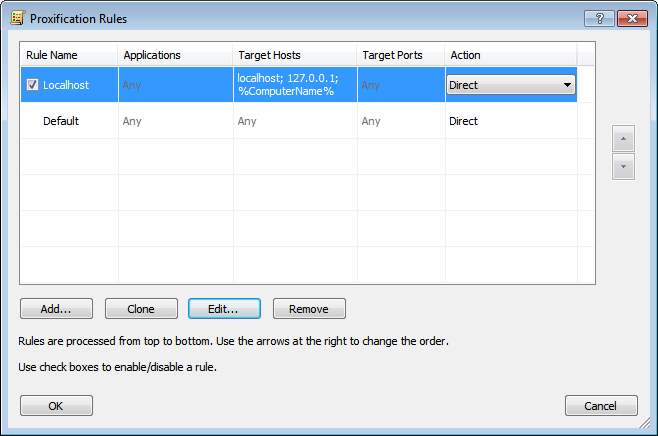
The “Default” rule cannot be changed. It is a special rule. Proxifier uses it when no other rules match the connection. You can only change the action for this rule.
For example, if you assign a proxy server as an action for the “Default” rule and you have no more rules defined, Proxifier will process all connections through this proxy.
By default each profile also has a predefined rule called “Localhost.” When this rule is enabled, Proxifier does not tunnel local connections (loopbacks) on the computer. Some applications like Firefox can depend on the loopback connections. You can edit or remove this rule, but it is recommended to keep it enabled unless you are absolutely sure that you need to tunnel connections to 127.0.0.1 through a proxy.
Proxifier scans rules from top to bottom. Thus, the rule order is important. You can change the order with the arrow-like buttons on the right side of the window.
You can enable/disable the rules with the check box and change the rule’s action.
With the corresponding buttons it is possible to Add a new rule, Clone, Edit or Remove an existing rule. Alternatively, you can use double-click to edit a rule or the “Del” key to remove it.
When you edit a rule or add a new one the following window appears:
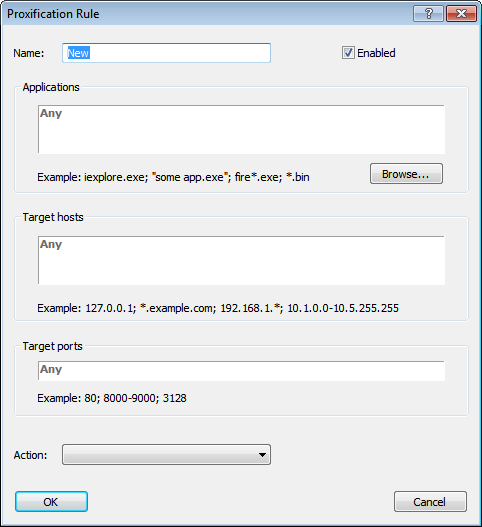
Name — the name of the rule. You can use any text that is meaningful for you.
Enable — use this check box to enable/disable the rule. When the rule is disabled, Proxifier simply ignores it.
Applications — a list of executable file names that correspond to the programs which connections should match the rule.
Separate individual names with a semicolon (;). Use double quotes (") for names containing spaces.
You can use wildcards (masks) where “?” matches any symbol and “*” matches any substring. The path of the file is not relevant.
With the Browse... button you can browse for the file and add it to the list.
Target hosts — to match the rule a connection should connect to a host from this list.
You can specify host names (DNS names), IPv4 or IPv6 addresses.
Separate individual addresses with a semicolon (;). Wildcards (masks) are supported and you can use wildcards (masks) where “?” matches any symbol and “*” matches any substring.
IPv4/IPv6 addresses can be specified as a range. Use a minus sign (-) to define the range.
%ComputerName% constant is automatically swapped with the local computer name during the processing.
Target ports — to match the rule a connection should connect to a port from this list.
You can use any integer from 1 to 65 535 (2^16-1). Separate individual ports with a semicolon (;).
Use a minus sign (-) to define a range.
Action — defines how Proxifier should process the connection if it matches the rule.
Possible options:
Proxy <name> — process the connection through the proxy server. You can define proxy servers at Profile->Proxy Servers...
Chain <name> — process the connection through the proxy chain. You can create proxy chains at Profile->Proxy Servers...
Direct — process the connection directly (skip any processing). The connections will be connected to the original target.
Block — the connection will be blocked.
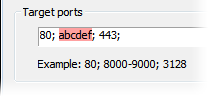
Proxifier applies certain filtering for the text fields. Incorrect symbols are indicated with red color. For example, there can be no letters in Target ports field:
To match the rule a connection should satisfy all three criteria: Applications, Target hosts and Ports. If you have nothing defined in a field, the word “Any” in gray color is displayed and it will then match all possible values for certain criteria. This effectively means that this criterion will not be used for rule valuation.
For example, if you specify Applications only and leave Targets and Ports empty, Proxifier will process all connections of the specified applications regardless of the target hosts and ports.
Note:
The rules have no effect on manually proxified applications (“Proxifier” command in the context menu of exe-files). In other words, applications started by the “Proxifier” command will always be redirected through a proxy server.



